Introduction: The Science Behind Plastic Sheets
Plastic sheets are everywhere in our lives — from kitchen cutting boards and automotive interiors to protective panels in industrial equipment. But have you ever wondered how these durable, perfectly flat sheets are made from simple plastic pellets?
1.Choosing the Right Raw Material
The first step in plastic sheet manufacturing is selecting the right resin. Common materials include:
PP (Polypropylene): Lightweight, chemical-resistant, and easy to fabricate.
PE (Polyethylene): Durable, impact-resistant, and food-safe.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Rigid, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant.
PC (Polycarbonate): Transparent and impact-resistant.
ABS: Tough and easy to mold, ideal for mechanical parts.
The choice depends on the application — for example, PE sheets are popular in food processing, while UHMW sheets excel in machinery applications due to their superior wear resistance.
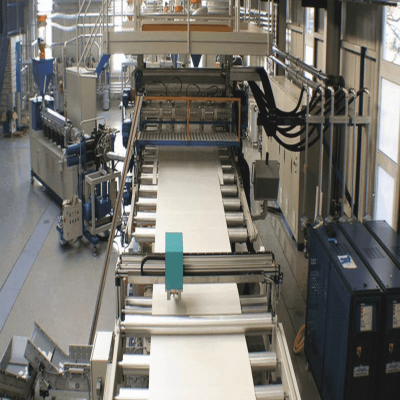
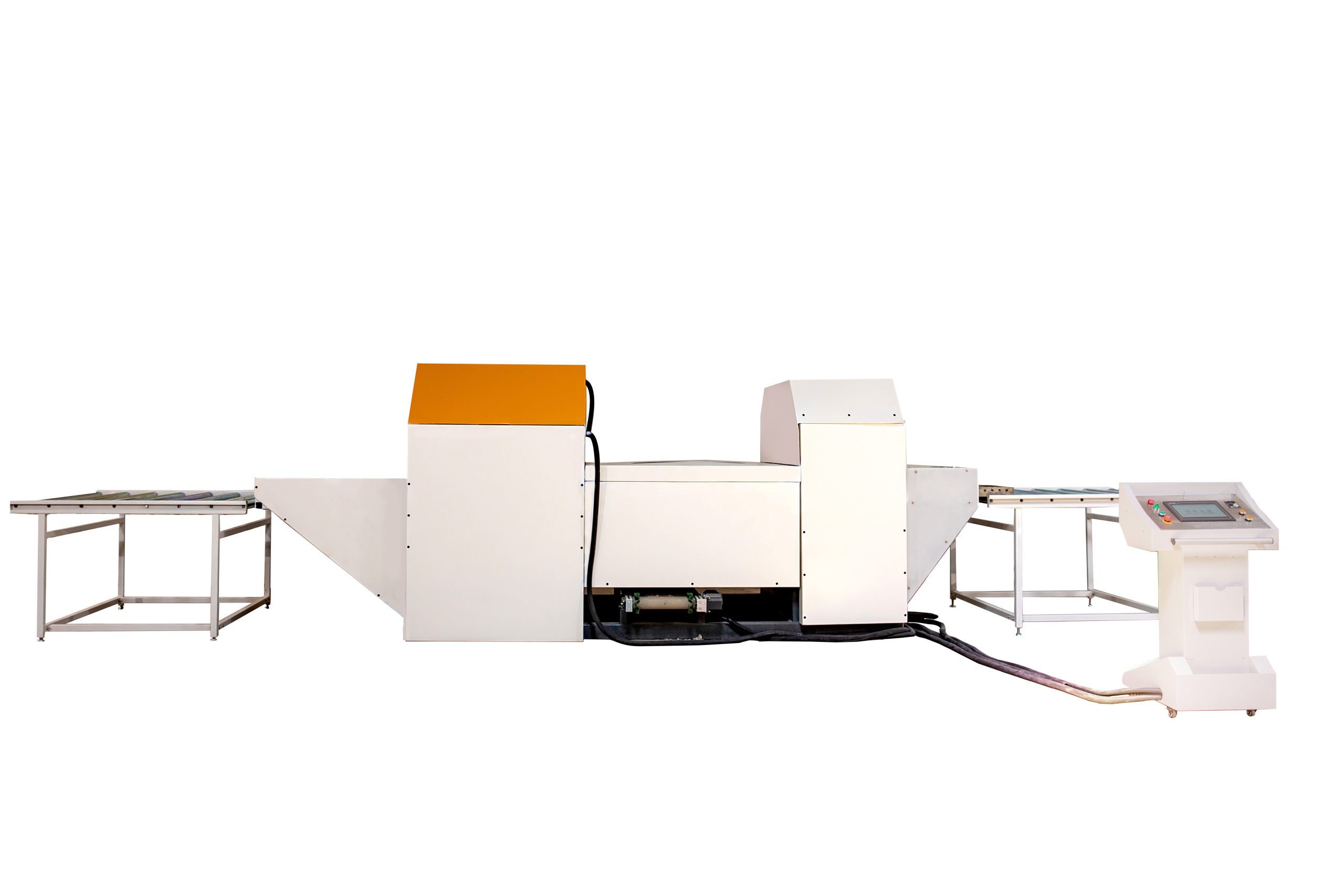
2.Extrusion — Turning Pellets into Flat Sheets
Once the raw material is chosen, plastic pellets are fed into an extrusion line. The process involves:
Heating and Melting: Pellets are melted under high temperature.
Extrusion: The molten plastic is pushed through a die, forming a continuous sheet.
Cooling and Calibrating: Cooling rollers flatten and solidify the sheet surface.
This stage defines the sheet’s thickness, smoothness, and dimensional accuracy. Advanced extrusion lines produce sheets with uniform structure and minimal internal stress.
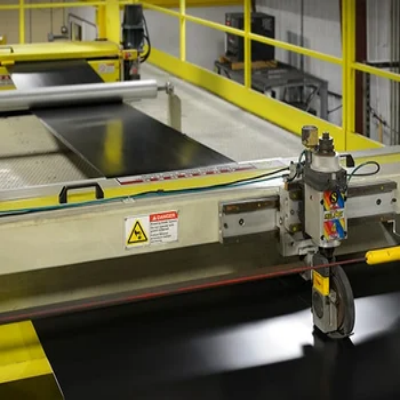
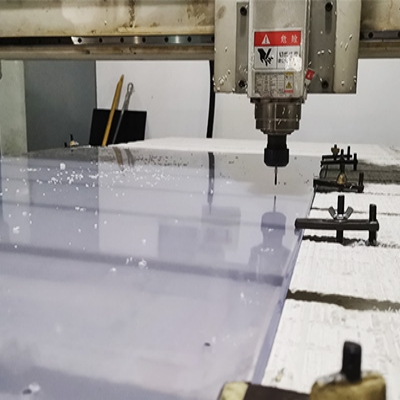
3.Post-Processing — Precision and Customization
After extrusion, sheets go through secondary processing depending on customer needs:
Cutting and Engraving: CNC machines ensure precision shaping.
Welding and Bending: Ideal for structural components and tanks.
Drilling and Thermoforming: Creates special forms and functional products.
Manufacturers often provide surface finishing — matte, embossed, or textured — and functional additives such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, or anti-static properties.
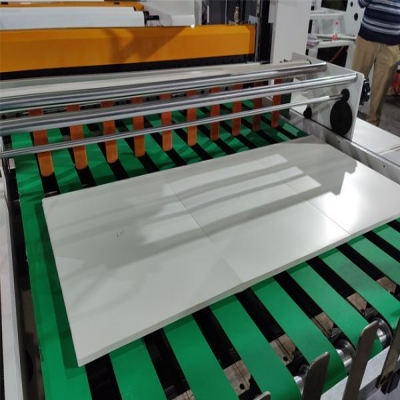
4.Quality Inspection and Packaging
Before shipping, each batch is tested for:
Thickness and flatness
Tensile strength and impact resistance
Chemical and weather durability
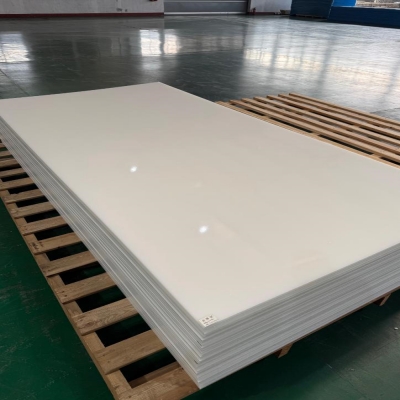
Sheets are then trimmed, covered with protective film, and packed securely to prevent scratches during transport.
5.Sustainability and Recycling
Modern manufacturers emphasize sustainability. Production scrap and offcuts are often recycled, and many materials such as PE and PP are fully recyclable.
Energy-efficient extrusion systems and low-carbon production processes are becoming standard practices in the industry.
The Birth of a Plastic Sheet
A plastic sheet is more than just melted resin — it’s a product of engineering precision, material science, and sustainability.
Every stage — from raw material to finished sheet — contributes to its strength, appearance, and performance.
Next time you see a plastic sheet, take a moment to appreciate the craftsmanship and technology behind it.