In today’s manufacturing and engineering world, plastic rods have become a go-to material for designers, OEMs, and maintenance teams who want strong, lightweight, and cost-effective alternatives to metals. Whether you are producing food-safe components, precision machined parts, or corrosion-resistant fittings, plastic rods offer a versatile base material. This article explores the main types of plastic rods, their key properties, and the benefits they deliver to businesses and end users.
1.What Are Plastic Rods?
Plastic rods are solid, cylindrical extrusions or cast profiles made from thermoplastics or engineering plastics. They are typically produced in standard lengths and diameters but can also be cut, machined, or fabricated to custom specifications. Common uses include bearings, bushings, gears, spacers, and structural components where metals are too heavy, too expensive, or prone to corrosion.
For international buyers or engineers sourcing raw materials, understanding the differences between various plastic rod types ensures optimal performance, regulatory compliance, and cost control.
2.Main Types of Plastic Rods
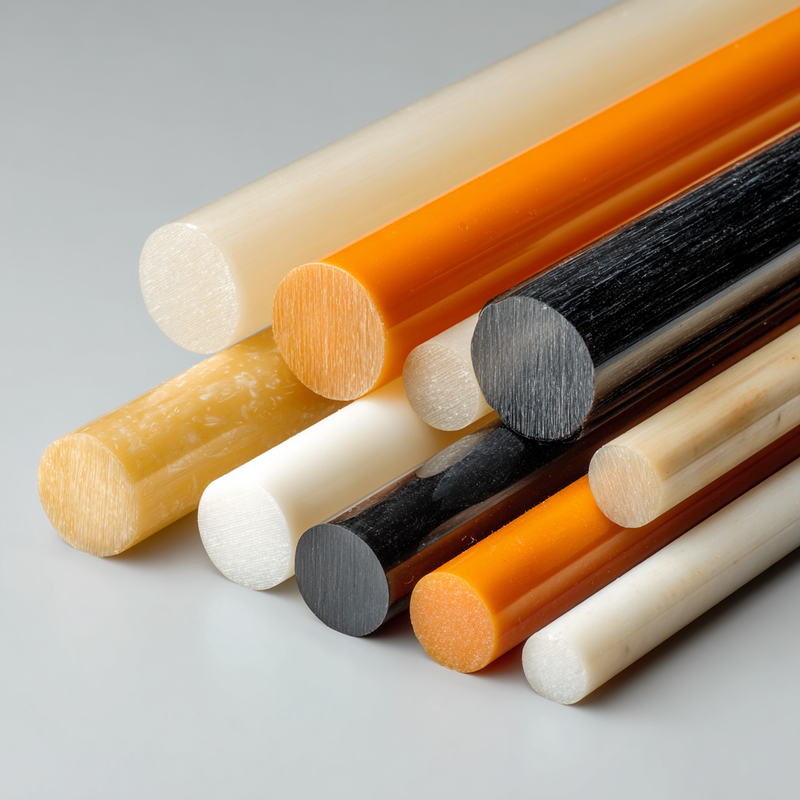
Plastic rods are not all created equal. Below are some of the most widely used types, along with their distinguishing features:
1. Nylon (PA6/PA66) Rods
Nylon rods are known for their excellent mechanical strength, wear resistance, and low friction coefficient. They are ideal for gears, rollers, and sliding elements in conveyors. With heat-stabilized grades available, nylon rods can handle continuous temperatures around 100–120 °C.
2. Acetal (POM/Delrin®) Rods
Acetal or polyoxymethylene rods provide high stiffness, dimensional stability, and fatigue resistance. They are often used in precision parts, such as valve components, pump housings, and automotive clips. Because of their low moisture absorption, POM rods maintain tight tolerances even in humid conditions.
3. Polypropylene (PP) Rods
Lightweight and highly resistant to chemicals, PP rods are widely used in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food-processing sectors. They are ideal for tank fittings, pipe supports, and components exposed to acids, alkalis, and solvents.
4. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and UHMW-PE Rods
HDPE rods provide an economical option for general-purpose applications, while ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMW-PE) rods excel in extreme wear conditions. They are commonly used in conveyor systems, chute liners, and impact-resistant parts.
5. Acrylic (PMMA) Rods
Acrylic rods are prized for their glass-like clarity and aesthetic appeal. They are often found in displays, lighting, and architectural features where transparency and UV stability matter.
6. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Rods
Rigid PVC rods combine good mechanical strength with chemical resistance and cost efficiency. They are used in industrial equipment, laboratory benches, and components where corrosion resistance is critical.
3.Key Properties of Plastic Rods
When selecting a plastic rod, consider the following technical properties to ensure the material matches your application:
1.Mechanical Strength: Engineering plastics like nylon and POM can rival metals in load-bearing capacity for many applications.
2.Wear and Abrasion Resistance: UHMW-PE and nylon rods offer excellent sliding properties, reducing maintenance on moving parts.
3.Chemical Resistance: PP and PVC rods withstand harsh acids, alkalis, and cleaning agents, making them suitable for chemical processing.
4.Moisture Absorption: Low-absorption materials such as POM maintain dimensional stability in humid or wet environments.
5.Thermal Performance: Check the continuous-use temperature and short-term heat limits of each material to prevent deformation or loss of strength.
6.Electrical Insulation: Many plastic rods provide high dielectric strength, making them useful in electrical and electronic applications.
By understanding these parameters, engineers and buyers can choose the right material grade and avoid premature failure or compliance issues.
4.Benefits of Using Plastic Rods
Switching from metal or other traditional materials to plastic rods can deliver a wide range of benefits:
1. Lightweight and Easy to Handle
Plastics weigh significantly less than metals, reducing shipping costs and making installation easier. This also improves energy efficiency in moving machinery parts.
2. Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Unlike metals, plastic rods do not rust and can withstand aggressive chemicals, water, and cleaning agents. This leads to longer service life and lower maintenance costs.
3. Excellent Machinability
Most plastic rods can be sawed, drilled, turned, milled, or fabricated with standard equipment. This makes them ideal for custom parts, small batches, or prototyping without expensive molds.
4. Noise and Vibration Reduction
Plastic components often dampen noise and absorb vibration better than metal, enhancing operator comfort and extending equipment life.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Many plastic rods are available in FDA-approved or EU food-grade versions, meeting strict hygiene and safety standards for food, medical, and pharmaceutical applications.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
Although some high-performance plastics carry a higher unit price, the overall lifecycle cost—including reduced maintenance, longer service life, and easier fabrication—often makes them more economical than metal alternatives.
5.How to Choose the Right Plastic Rod
Choosing the right plastic rod involves balancing performance requirements, regulatory needs, and budget. Here are some practical tips:
- Define the Operating Environment: Temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical load are critical parameters.
- Check Compliance Requirements: If the part contacts food or pharmaceuticals, verify FDA, EU, or other certifications.
- Evaluate Machining and Fabrication Needs: Some plastics respond better to certain machining methods; consult your supplier for recommended processes.
- Consider Color and Additives: Color coding can improve safety and process control; additives can enhance UV stability or flame retardancy.
- Request Samples or Small Batches: Testing a small quantity can prevent costly mistakes before full-scale production.
Working closely with a reliable manufacturer or distributor can help you navigate these choices and secure consistent quality.
Conclusion
Plastic rods are a cornerstone material for countless industrial and commercial applications. By understanding the types, properties, and benefits of different plastics, buyers and engineers can make informed decisions that improve performance, compliance, and cost efficiency. Whether you need high-strength nylon rods for mechanical parts, FDA-compliant PP rods for food processing, or clear acrylic rods for architectural projects, there is a plastic rod solution to fit your needs.
Partnering with a manufacturer that offers a full range of materials, diameters, colors, and custom machining options ensures you receive not only the right product but also the technical support to maximize its performance.